
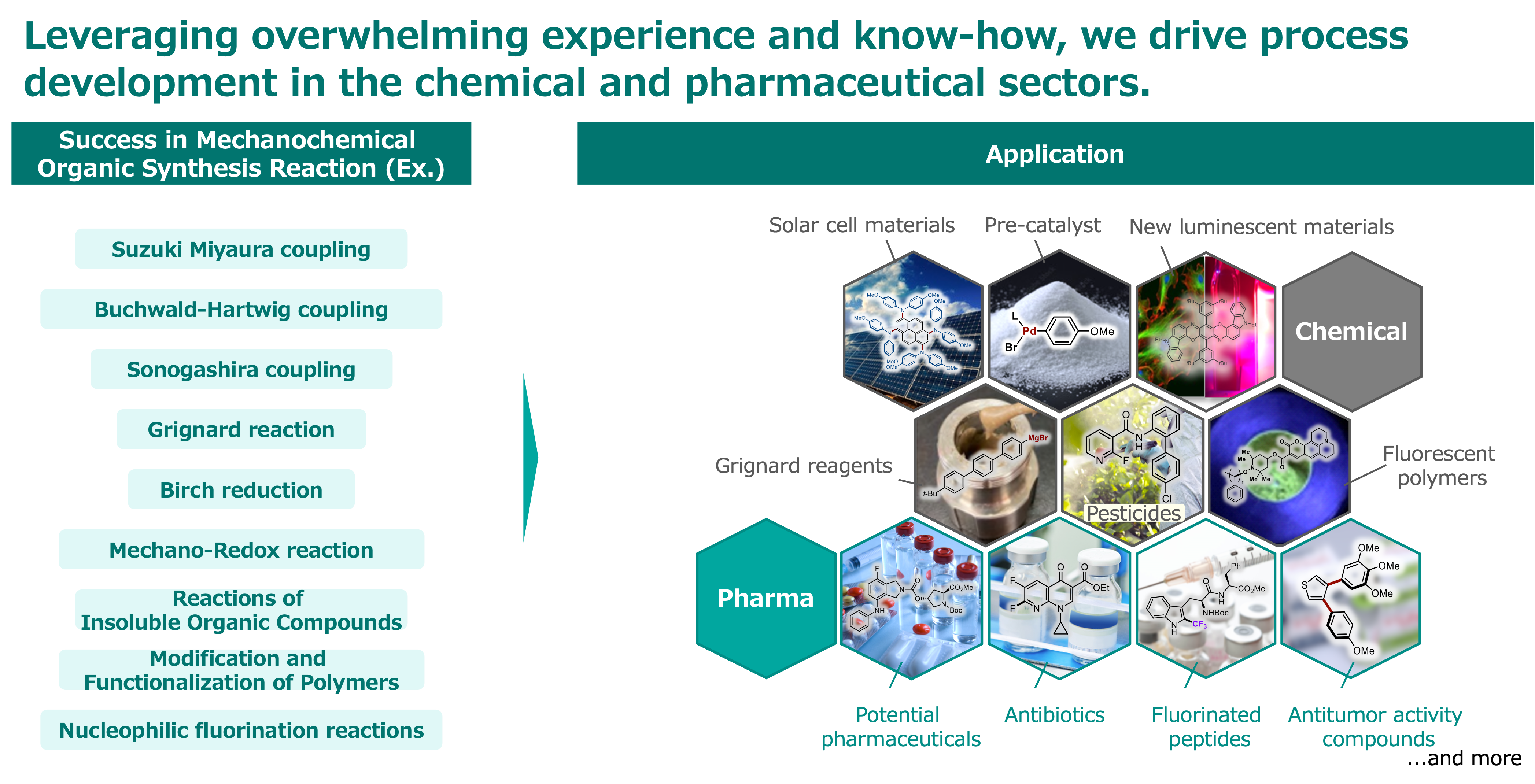
About Mechano Chemistry
Organic synthesis is an important technology to create medicines and high functional chemical materials over the last 100 years. However this has a drawback, it needs a large amount of petroleum-derived organic solvents.
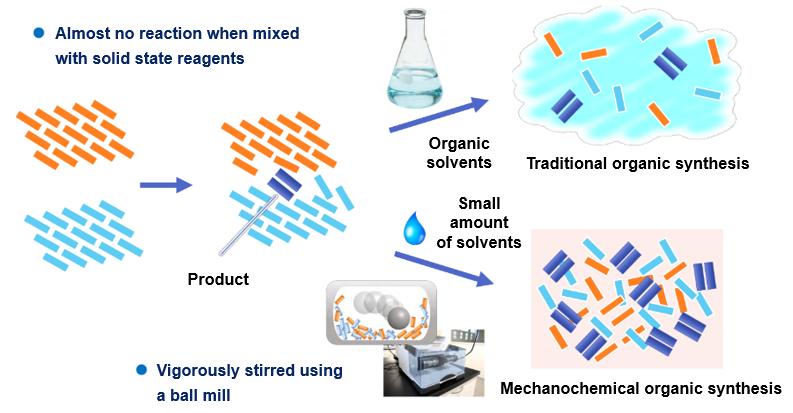
Mechanochemical organic synthesis using a stirring device such as a ball mill allows for a significant reduction in the amount of organic solvent in the reaction, faster reactions, simpler operations and lower costs compared to conventional solution-based reactions.
Furthermore, mechanochemical organic synthesis is an innovative technique with new possibilities in organic chemistry, as insoluble compounds can also be used in reactions.
Advantages of mechanochemical organic synthesis
-
Enabling a significant reduction in organic solvents.
-
Miniaturization of synthetic equipments
-
Significantly reduced the reaction times.
-
Cost reduction including personnel
-
Functionalization of poorly soluble compounds
-
Efficient activation of bulk metals.
-
Functionalization or degradation of various polymers
-
Simple reaction operation (no need for inert gas)

What Can Mechanochemistry Do For Human Society?
Mechano Chemistry
01
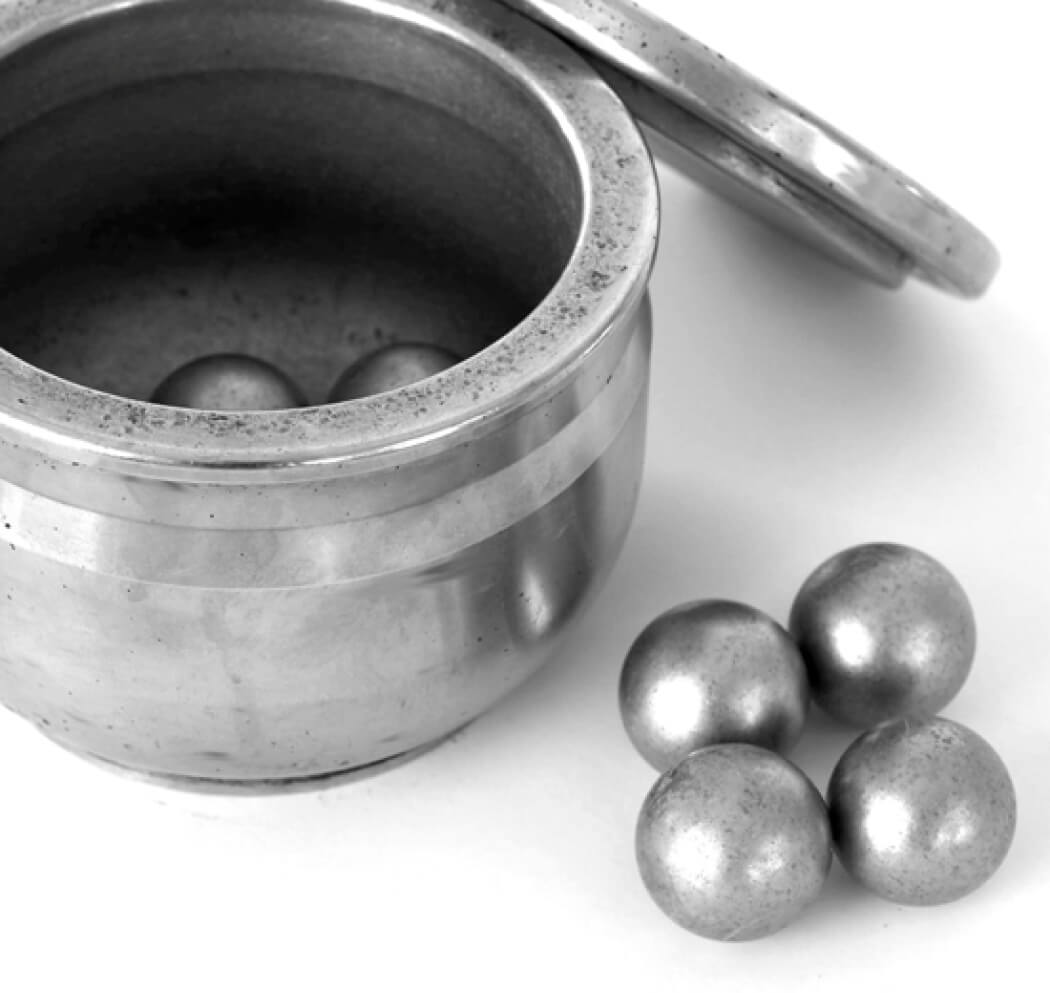

What is Mechanochemical Organic Synthesis?
Mechanochemical organic synthesis is a new technology that uses a mechanical stirring device such as a ball mill to perform organic synthesis reactions. This technology has the potential to significantly advance organic synthesis by allowing reactions with poorly soluble compounds (unused materials) that are difficult to handle in conventional solution-based organic synthesis.
02

Environmental Friendliness through Mechanochemical Organic Synthesis
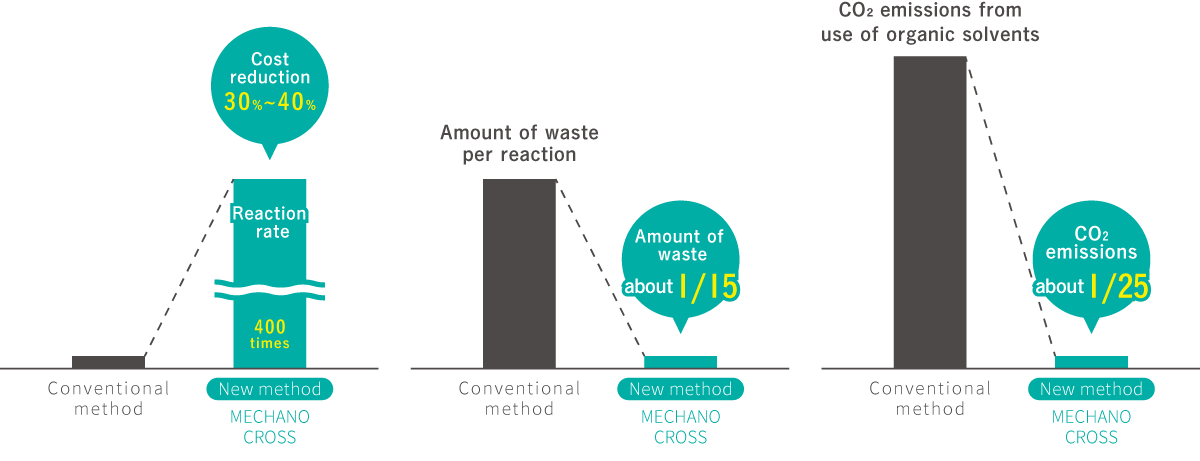
Environmentally friendly and sustainable organic synthesis is possible through our technology because the amount of organic solvents that cause CO₂ emissions can be reduced by mechanochemical synthesis. The amount of organic solvents used in the various reactions can be reduced to less than 1/15.
03

Mechanochemical Organic Synthesis Enables Mush Faster Reactions
Organic synthesis can be performed without solvents or at high concentrations under mechanochemical conditions, which dramatically shortens the reaction time compared with conventional synthetic reactions in solution. For example, the Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction, which requires 24 h, can proceed in 5 min (approximately 1/300 the time of the conventional method).
Achievements and Awards

Representative Director / President & Chief Executive Officer
Tomohisa Saito CEO
- 2023 North Pacific Bank Start-up R&D Fund awarded.
- 2024 Research and development grant adopted by Mitsubishi UFJ Technology Development Foundation
- 2024 Independent's Club Spring Pitch Bronze Award

Director / Member of the Board & Technical Advisor
Professor Hajime Ito
- 2022 HSFC DemoDay Hokkaido Governor's Award
- 2023 HSFC DemoDay Hokkaido Governor's Award
- Winners of The Chemical Society of Japan Award for 2024

Director / Member of the Board & Technical Advisor
Associate Professor Koji Kubota
- 2022 MechSustInd International Award (International Newcomer Award in the field of mechanochemistry.)
- 2023 The Chemical Society of Japan Award for Young Chemists (Pioneering and Developing Solid-State Mechano-Organic Synthetic Chemistry)
- Chemist Award BCA 2024
- Received the Hokkaido Science and Technology Encouragement Award in FY2024
- Received the Young Scientist Award of the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Commendation in the field of science and technology in FY2025

Director / Member of the Board & Technical Advisor
Associate Professor Koji Kubota
- Second Prize winner at the Shenzhen Innovation Pitch Competition 2024 Japan Tournament
- 1st place winner at the Global Pitch Stadium (Environmental Energy Field) at the Environmental Energy Innovation Summit LEEP SUMMIT 2024
- J-Startup X Demo Day Pitch Winner
- Selected as a semi-finalist in the SusHi Tech Tokyo 2025 pitch competition "SusHi Tech Challenge 2025"
Technology
MECHANOCROSS Co., Ltd. provides mechanochemical process to replace your proposed solution-based reactions with our unique patented technology. Specifically, we aim to achieve the desired conversion, yield, and selectivity for your specific requests, from reaction feasibility to optimization of reaction conditions. We will work closely with the Laboratory of Organoelement Chemistry, Hokkaido University, with whom we are collaborating, to develop novel mechanochemical organic synthetic reactions quickly. We are ready to carry out mechanochemical organic synthesis at various scales and are providing to diverse needs of partners as much as possible.
What's mechanochemical organic synthesis?
Conventional organic synthesis methods are generally solution methods that use large amounts of organic solvents and agitation for the purpose of efficiently carrying out target reactions. In contrast, mechanochemical organic synthesis using a stirring device such as a ball mill is a new technology that utilizes highly efficient stirring and requires almost no organic solvents.
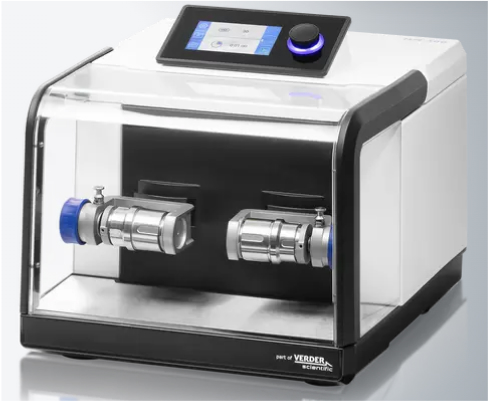

MM400 Mixer mill
A general mixer-mill device with high grinding power. Reaction vessels (called jars) are 1.5~50 mL in size and used for lab-scale studies. Jar materials include hardened steel, stainless steel, tungsten carbide, agate, zirconium oxide, PTFE, PMMA, etc., and can be adjusted to suit reaction conditions.
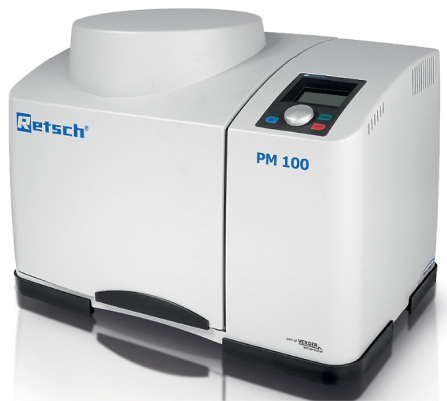

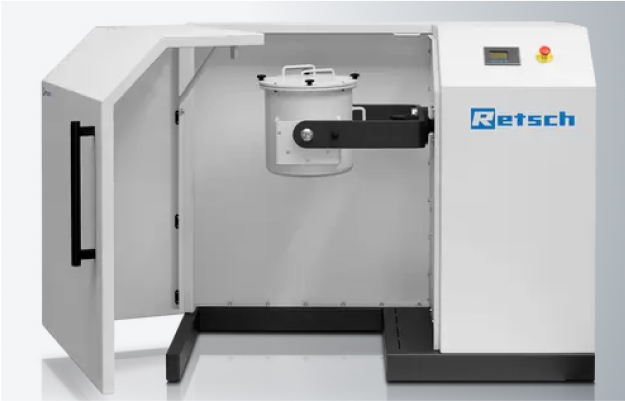
PM100 Planetary ball mill
This mill device utilizes centrifugal force at high speed rotation and also has high milling power. Reaction vessels (called jars) range in size from 12 to 500 mL and are used for larger scale reactions than mixer type. Jars are made of hardened steel, stainless steel, tungsten carbide, agate, sintered aluminum oxide, silicon nitride, and zirconium oxide.

TM300 Drum mill
This is a large scale mill system capable of ball and rod milling. It has the grinding power of a mixer mill or other mills, but with jar sizes from 5~43.4 L, and can also react on larger scales. Jars are generally made of stainless steel.
Potential
New materials development from insoluble materials.
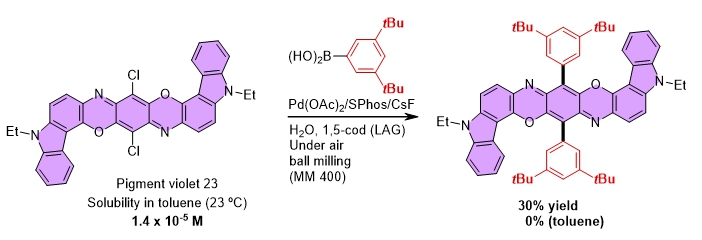
In mechanochemical organic synthesis, compounds do not need to be completely dissolved, and reactions can proceed with only a small amount of organic solvent. This means that compounds with poor solubility, which have been avoided until now, can be used in mechanochemical organic synthesis. In fact, Dr. Ito and Dr. Kubota at Hokkaido University have succeeded in developing a cross-coupling reaction using pigments, which are representative of insoluble substances, as substrates. This means that mechanochemical organic synthesis has the potential to revolutionize and evolve the world of organic synthesis, which has continued for more than 100 years.
Technology to maximize the potential of bulk metals.
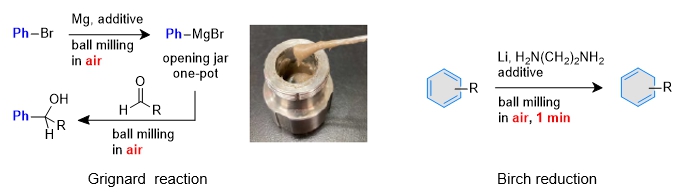
In organic synthesis using bulk metals, metal surface activation and the water content of the reaction solvent can greatly reduce reproducibility. Therefore, existing methods have "required" the use of additives that activate the metal surface and the use of reaction solvents after dehydration. However, in this mechanochemical organic synthesis reaction, the metal surface is activated by strong stirring force, and the reaction proceeds efficiently without additives. In addition, since only a very small amount of reaction solvent is added, the desired compound can be obtained reproducibly in air without solvent dehydration. This characteristic enables ultra-fast Birch reduction without the need for paste Grignard reagents or ammonia, which can be operated in air.
Summary of possible reactions
In the mechanochemical organic synthesis process, the new method achieves almost 100% in 5 min, compared to only 60% in 24 h under conventional solution-based conditions. The amount of waste per reaction is about 1/15 of the conventional method, and CO2 emissions are about 1/25 of the conventional method, enabling a significant cost reduction. (Comparison with Suzuki-Miyaura cross coupling)
Examples of mechanochemical reactions
Mechanochemical nucleophilic aromatic fluorination. Those listed above are also available, please contact us.

